Point in the Second quadrant
Point P is 30 mm above HP, 50 mm behind VP and 45 mm in front of left PP. Since point P is located behind VP, the VP is assumed transparent. The position of the point w.r.t the three planes are shown in Figure 1. The direction of viewing are shown by arrows. After projecting the point on to the three planes, the HP and PP are rotated such that they lie along the VP. The direction of rotation of the HP and PP is shown in figure 2. As shown in figure 3, after rotation of the PP and HP, it is found that the VP and HP is overlapping. The multi-view drawing for the point P lying in the second quadrant is shown in figure 4. Though for the projection of a single point, this may not be a problem, the multi-view drawing of solids, where a number of lines are to be drawn, will be very complicated. Hence second angle projection Technic is not followed anywhere for engineering drawing.
 |
| Figure 1. The projection of point P on to the three projection planes |
 |
Figure 2. The direction of rotation of HP. |
 |
Figure 3. The projection of point P after complete rotation of the HP and PP.
|
 |
Figure 4. The multiview drawing of the point P lying in the second quadrant.
Point in the Third quadrant Projection of a point P in the third quadrant where P is 40 mm behind VP, 50 mm below HP and 30 mm behind the right PP is shown in figure 5.
Since the three planes of projections lie in between the observer and the point P, they are assumed as transparent planes. After the point P is projected on to the three planes, the HP and VP are rotated along the direction shown in figure 6, such that the HP and PP is in plane with the VP. The orthographic projection of the point P lying in the third quadrant is shown in figure 7.
 | Figure 5. Projection of a point P placed in the third quadrant
In the third angle projection, the Top view is always above the front view and the Right side view will be towards the right of the Front view.
| Figure 6. shows the sense of direction of rotation of PP and HP.
Figure 7. Multi-view drawing of the point lying in the third quadrant. In the third angle projection, the Top view is always above the front view and the Right side view will be towards the right of the Front view. Point in the Fourth quadrant
If A point is lying in the fourth quadrant, the point will be below the HP and infront of the VP. The point is projected on to the respective projection planes. After rotation of the HP and PP on to the VP, it will be observed that that the HP and VP are overlapping, similar to the second angle projection. The multi-view drawing of objects in such case would be very confusing and hence fourth angle projection technique is not followed by engineers.
|
|
|







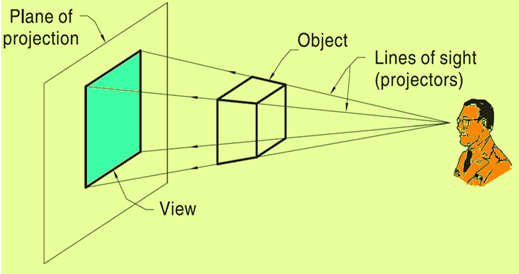

Comments
Post a Comment